Educational Materials on Wound Care
Understanding Wound Types and Treatment Options
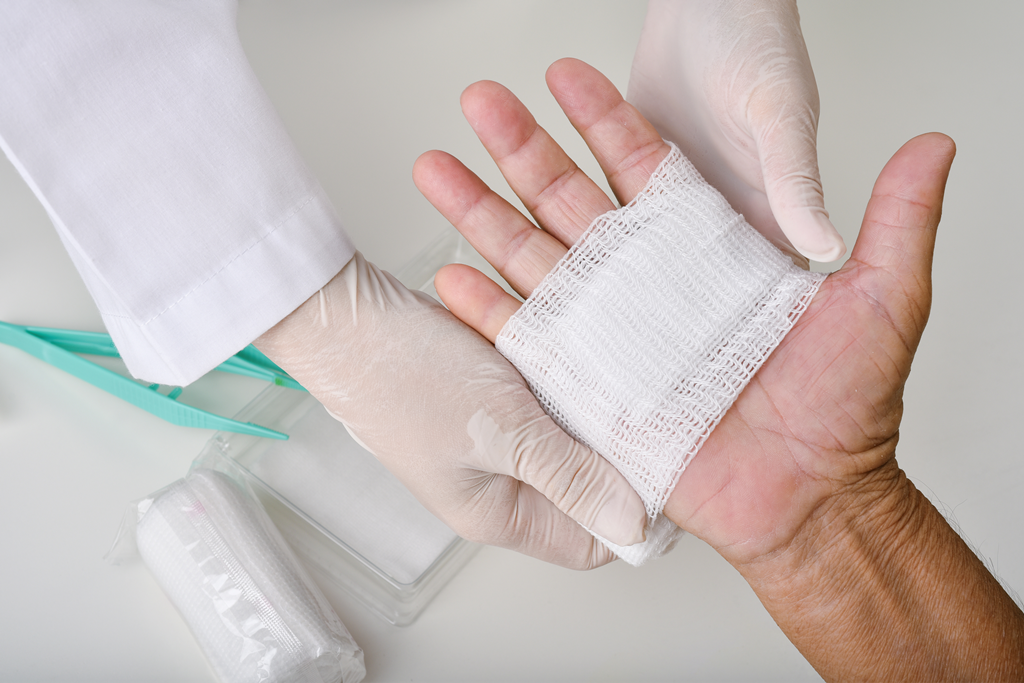
Wounds can occur for various reasons, ranging from minor cuts and abrasions to more serious injuries and medical conditions. Understanding the different types of wounds and their appropriate treatment options is essential for promoting proper healing and preventing complications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the common types of wounds, their causes, and the recommended treatment approaches to facilitate optimal healing and recovery.
Types of Wounds:
- Incision: These are clean, straight cuts typically caused by sharp objects such as knives or surgical instruments.
- Laceration: Irregular or jagged wounds caused by blunt trauma or tearing of the skin, commonly seen in accidents or falls.
- Abrasion: Superficial scrapes or grazes resulting from friction or rubbing against a rough surface.
- Puncture: Small, deep wounds caused by sharp objects puncturing the skin, such as nails or needles.
- Contusion: Also known as bruises, these are caused by blunt force trauma, resulting in damage to blood vessels beneath the skin.
- Burns: Injuries caused by exposure to heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation, varying in severity from minor to life-threatening.
Treatment Options:
- Cleaning and Debridement: Proper wound cleaning is essential to remove debris, bacteria, and dead tissue from the wound bed. Debridement may be necessary to remove necrotic tissue and promote healing.
- Dressing and Bandaging: Applying appropriate dressings or bandages helps protect the wound from further injury, maintain a moist wound environment, and facilitate healing.
- Topical Medications: Antiseptic solutions, ointments, and creams may be used to prevent infection and promote wound healing.
- Advanced Therapies: For chronic or non-healing wounds, advanced therapies such as negative pressure wound therapy, bioengineered skin substitutes, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be recommended.
- Pain Management: Managing pain associated with wounds is important for patient comfort and compliance with treatment. Analgesics and other pain-relieving modalities may be prescribed as needed.
By understanding the different types of wounds and their appropriate treatment options, patients and caregivers can play an active role in promoting healing and preventing complications. Educational materials on wound care empower individuals with the knowledge and resources they need to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Preventing Infections and Complications

Preventing infections and complications is a critical aspect of wound care management. Untreated or improperly managed wounds can lead to serious consequences, including infection, delayed healing, and even tissue necrosis. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore strategies for preventing infections and complications associated with wounds, empowering patients and caregivers with the knowledge and tools they need to promote optimal healing and recovery.
Prevention Strategies:
- Wound Hygiene: Proper wound hygiene is essential to prevent infections. Clean the wound with mild soap and water, and gently pat dry with a clean cloth.
- Dressing Changes: Regularly change dressings according to healthcare provider recommendations to maintain a clean and moist wound environment.
- Hand Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after handling wounds to reduce the risk of introducing bacteria.
- Protective Measures: Keep the wound covered with appropriate dressings or bandages to protect it from contamination and further injury.
- Nutrition:Maintain a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals to support the body’s natural healing processes.
- Smoking Cessation: Avoid smoking, as it can impair circulation and delay wound healing. Seek support and resources to quit smoking if needed.
- Monitor for Signs of Infection: Watch for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, warmth, or pus drainage, and seek medical attention promptly if present.
- Follow Healthcare Provider Recommendations: Adhere to prescribed treatment regimens and follow-up appointments to ensure proper wound care and monitoring.
By implementing these prevention strategies and staying vigilant for signs of infection or complications, patients and caregivers can help reduce the risk of complications and promote optimal healing and recovery. Educational materials on wound care provide valuable information and resources to empower individuals to take an active role in their health and well-being.
Supporting Patient Recovery and Rehabilitation
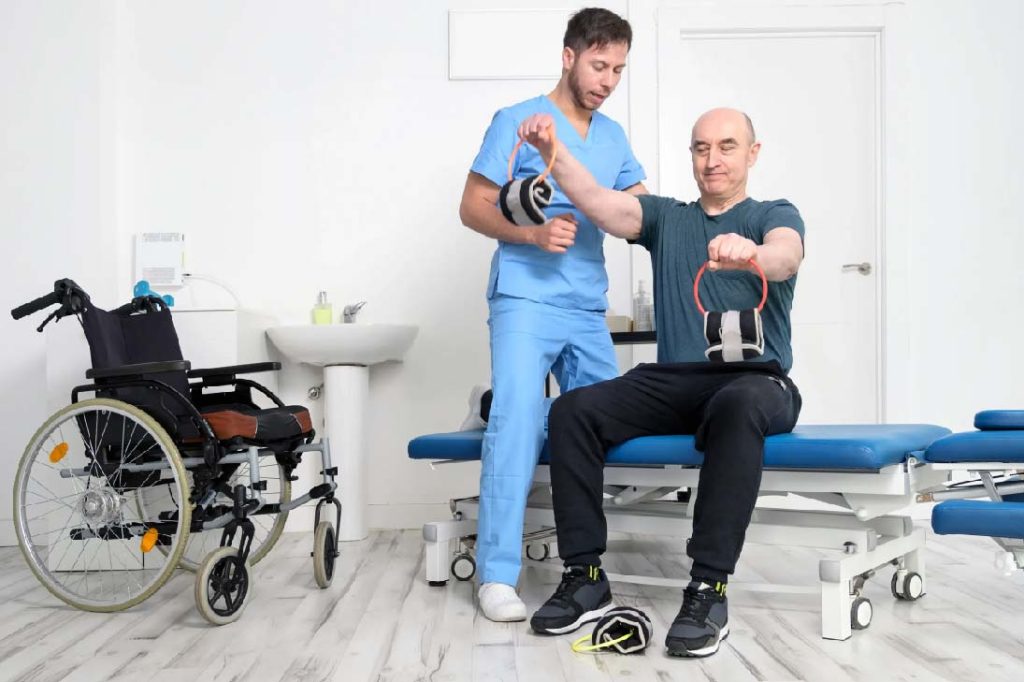
Supporting patient recovery and rehabilitation is a collaborative effort that involves healthcare providers, patients, and caregivers working together to promote healing and restore function. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore strategies for supporting patient recovery and rehabilitation following wound care treatments, empowering individuals with the knowledge and resources they need to achieve optimal outcomes and regain their quality of life.
Recovery Strategies:
- Follow Treatment Plan: Adhere to prescribed treatment regimens, including wound care protocols, medications, and rehabilitation exercises, as recommended by healthcare providers.
- Monitor Progress: Keep track of wound healing progress and report any changes or concerns to healthcare providers promptly.
- Maintain Mobility: Engage in regular physical activity within recommended limitations to promote circulation, strength, and mobility.
- Pain Management: Manage pain effectively with prescribed medications and non-pharmacological interventions to improve comfort and quality of life.
- Nutrition: Eat a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals to support tissue repair and recovery.
- Psychosocial Support: Seek support from family, friends, support groups, or mental health professionals to cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of recovery.
- Gradual Return to Activities: Gradually resume normal activities and responsibilities as tolerated, avoiding overexertion or activities that may compromise wound healing.
- Follow-Up Care: Attend scheduled follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor progress, address any concerns, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
By implementing these recovery strategies and collaborating closely with healthcare providers, patients and caregivers can support optimal healing and rehabilitation following wound care treatments. Educational materials on wound care provide valuable information and resources to empower individuals to navigate the recovery process and achieve the best possible outcomes.